At Least 200 Types of Bacteria Live in the Mouth, so Dentists and Doctors Call for Improving Oral Health
Oral diseases, despite being mostly preventable, represent a significant burden on the health sector of many countries and affect the population throughout their lives, causing pain, discomfort, deformities and even death.
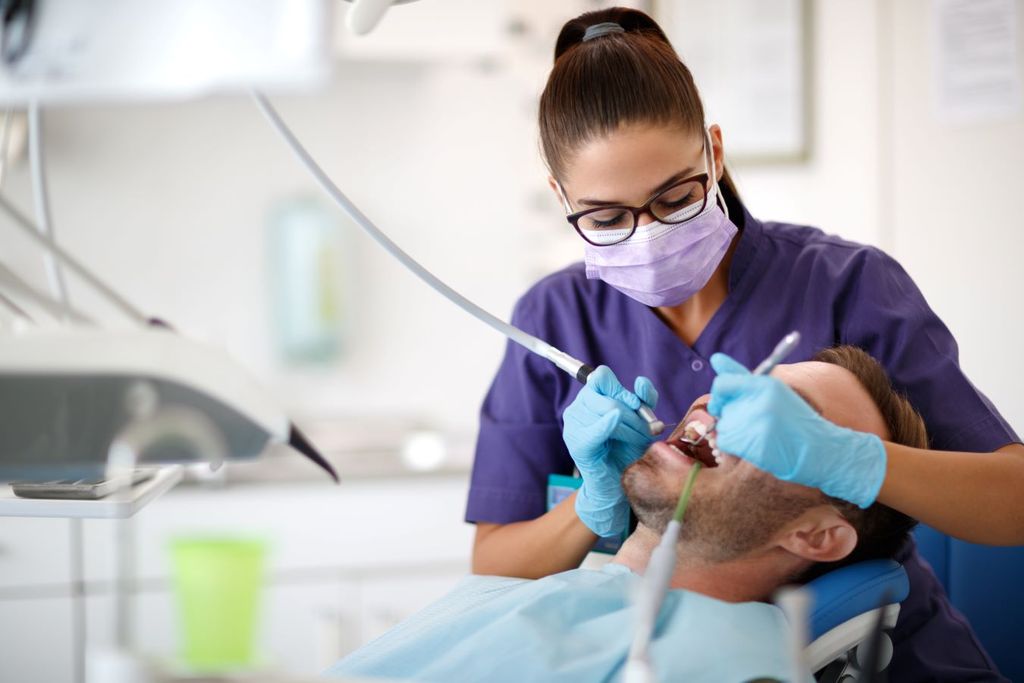
During the courtship and in the life of a couple, it is important to take actions to prevent the proliferation of diseases that can be transmitted orally, due to the accommodation of viruses and bacteria in the oral or dental cavity, said the stomatologist attached to the Family Medicine Unit. (UMF) No. 51 of the Mexican Social Security Institute (IMSS) in Jalisco, Turia Irazú Portugal Padilla.
The specialist recalled that there are different bacteria, viruses and fungi that can also manifest in oral diseases, and that can be transmitted through saliva or kissing between couples, for example influenza, flu, COVID-19, Epstein Barr virus or cytomegalovirus, herpes, cavities, gingivitis and even hepatitis A, gonorrhea and syphilis.
In addition, he mentioned that these diseases are highly transmissible, hence the importance of not sharing objects for personal use such as toothbrushes.
The specialist said that if the couple is not informed that you have cavities or gum disease or if you are a carrier of gonorrhea and syphilis, for example and your partner has a wound in the mouth (which are very common because of the sensitivity that is in it even if you have the best of hygienes), the probability of contagion of that disease is high, so in an act of love and social responsibility you must inform you promptly and of course take care of your oral hygiene.
According to the 2019 Global Burden of Disease Study (The Global Burden of Disease Study 2019), untreated dental caries in permanent teeth is the most common health disorder and it is estimated that these diseases affect almost 3,5 billion people worldwide.
Other oral conditions of importance for public health are oral fissures, noma (a serious gangrenous disease that begins in the mouth and mainly affects children) and strong blows either by car accidents, or by extreme or contact sports.
Oral diseases are increasing
The prevalence of the main oral diseases continues to increase around the world, but especially in developing countries such as Mexico, due to increasing urbanization and changes in living conditions. Also the insufficient use of fluoride and oral hygiene products such as toothpaste and dental floss.
The specialist reported that "sometimes in couples there is already so much trust and obvious coexistence that it is easy for them to borrow the toothbrush which is somewhat inappropriate, as well as sharing the glass of water or the same food, we should not normalize these behaviors."
A simple cavity should be treated as soon as possible since the infection can exceed the bloodstream and cause damage to other organs or sepsis.Likewise, the Epstein Barr virus and cytomegalovirus can cause from mild fevers and inflammation of the lymph nodes to affectations of the spleen and liver, if they are not treated in time and properly.
He urged the population to maintain optimal oral hygiene to prevent pathologies and infections, since he recalled that at least 200 types of bacteria are sheltered in the mouth and if there is immunosuppression which facilitates these affectations.




