Astronomers baffled by accidental discovery of starless galaxy
A galaxy is a collection of stars with gas, dust, dark matter, and a supermassive black hole at the center. What happens when a galaxy has no stars?

What defines a galaxy? In general, for astronomers, galaxies are structures made up of stars, dust, gas, dark matter, and a supermassive black hole in the center. How these structures are formed is perhaps one of the great open questions of astronomy.
This question even has its version: which came first, the chicken or the egg? The astronomical version is: which came first, the supermassive black hole or dark matter? This is a question that the JWST telescope's main mission is to answer and it has already been showing results since 2022.
¿Qué tan grande es la galaxia Andrómeda?
— Somos Cosmos (@InformaCosmos) January 12, 2024
Aquí hay una imagen en primer plano de la galaxia, cada punto es una estrella: pic.twitter.com/aixYRXDMQq
Astronomers have found a galaxy that has no stars, only gas. This type of galaxy is called a primordial galaxy. Some of the first galaxies in the universe are expected to become a cloud of gas without forming stars. The discovery may give some clues about how they formed and how they evolved.
Reviewing basic concepts about galaxies
The definition of a galaxy is usually that of a system made up of stars, gas, dust, and dark matter. It is now known that most galaxies have a supermassive black hole at their center. Supermassive black holes have become an important component of the definition of a galaxy.
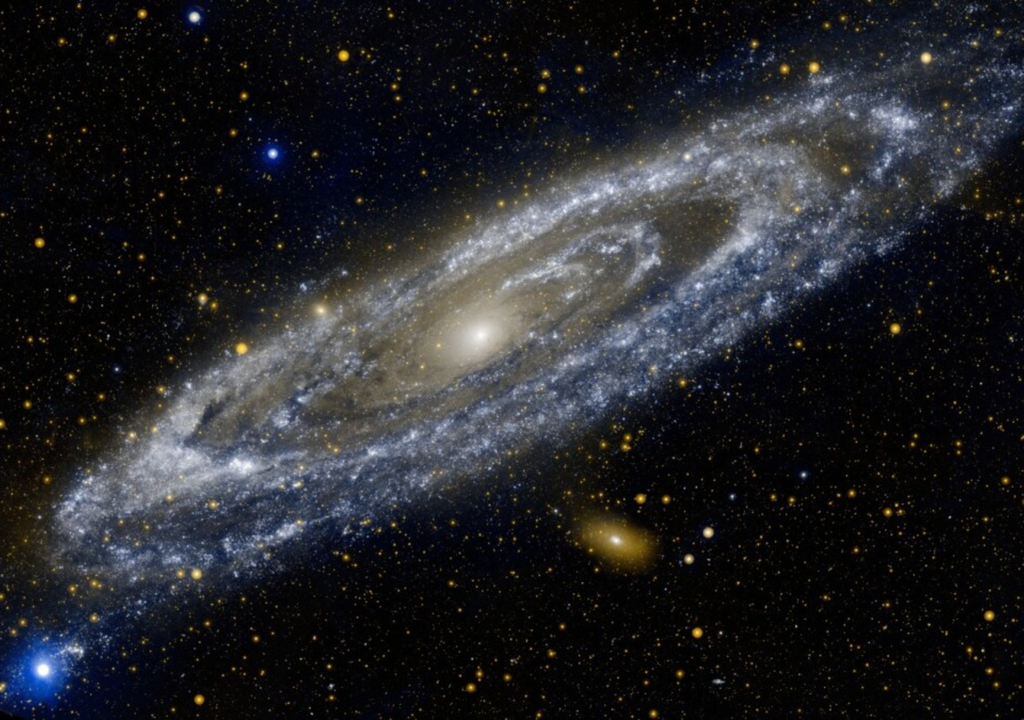

In the universe, several types of galaxies vary in size, shape, and mass. The best-known are spirals and ellipticals. Spiral galaxies have arms that curl like a spiral: our Milky Way is an example. Ellipticals, on the other hand, look like giant clouds with a shape reminiscent of an ellipsoid.
How are galaxies formed?
Wherever we look, we see galaxies. The further we look, the further back into the universe we can see, since that is the time it took for the emitted light to reach us. Today it is possible to observe back to when the universe was a few hundred million years old with James Webb.
Curiously, at that time, hundreds of millions of years ago, it is believed that the first galaxies began to form. One of the main missions of the JWST telescope was to observe the formation of these first galaxies and answer questions about how the formation process takes place.
There are different hypotheses about how a galaxy forms. One is that a supermassive black hole in a dark matter halo attracted stars. Another is that the dark matter halo attracted the stars and also the supermassive black hole that was pushed towards the center. It remains an unanswered question.
This is how they evolve
Although we do not know exactly how the formation occurred, we do have observations of how these galaxies evolved. It is even possible to know that for a redshift close to 2, a peak of star formation occurred in the galaxies. Observations at lower redshifts show some structures.
Redshift occurs when an object emits light and its length lengthens due to the expansion of the universe. Through the redshift, it is possible to know the distance and age of the universe when the light was emitted.
In general, in these cases, there are two types. One is when the galaxy stops forming stars and becomes a faint galaxy. Another is when gravitational interactions, such as collisions, alter the structure of the galaxy as it evolves. A third type would be a galaxy that has stopped forming stars and no longer has any.
The galaxy without stars: J0613+52
The search for these starless galaxies, called dark galaxies, has been underway for years. In recent years, galaxies with few stars have been found, but none fit the classification of a true dark galaxy. By accident, the Green Bank telescope observed the first dark galaxy.
Astrónomos descubren una galaxia aparentemente sin estrellas.
— Plano Informativo (@Planoinforma) January 13, 2024
Esta galaxia J0613+52, sin estrellas visibles, fue presentada en la 243ª reunión de la Sociedad Astronómica Estadounidense.
A pesar de su apariencia normal, este objeto único parece aislado e intacto, lo que desafía pic.twitter.com/ckLkMbqc2x
The accident occurred because the Green Bank telescope was observing a region famous for having no structures of interest. However, it was possible to find signals in the received data: a structure existed in that region. The signal was that there was a large amount of neutral hydrogen.
The most surprising thing is that there are no other galaxies in the surrounding area, indicating that J0613+52 has been isolated for a long time. This would be another indication that we are observing a dark galaxy without stars.
What does this mean for astronomy?
The galaxy J0613+52 indicates a third type of fate that galaxies can have during the evolution of the universe. In this case, it could be a very old galaxy that has stopped forming stars and the gas we observe is the so-called primordial gas.
Understanding the fates that a galaxy can have is essential to understanding how galaxies evolve since their formation. And perhaps answer questions about your own training.