
Although their shape may be reminiscent of the pyramids of Egypt and spark countless theories, these structures are masterpieces of nature, patiently sculpted by time.

Cindy Fernández studied a Bachelor's Degree in Atmospheric Sciences, with an orientation in Agrometeorology, at the University of Buenos Aires/a>. Since the first years of her meteorology career, she volunteered in different scientific dissemination activities, inside and outside the university.
Since 2015, she has been part of the National Meteorological Service's Press and Citizen Communication team, where she was trained as a, donde se formó como weather communicator. In addition to being the spokesperson of the organisation, she is also part of the editorial committee of Meteoros Magazine and the social networks team. For more than 5 years she has been featured in different media and participated as a guest meteorologist in different news programs.
For the third season, she participates as a columnist in the popular science program La Liga de la Ciencia, on public TV, where she deals with issues related to weather phenomena and climate change.
At the beginning of 2019, she joined the team of professionals at Meteored Argentina, where she works as a news editor.

Although their shape may be reminiscent of the pyramids of Egypt and spark countless theories, these structures are masterpieces of nature, patiently sculpted by time.

They found a new type of yeast from the digestive tract of bees that produces reduced-calorie beers. Will it taste similar to those on the market? This is what the study says.

New research suggests that the melting of Antarctic ice has consequences on the speed of planetary spin and that there is a need to discuss how to adjust the “UTC” standard time.

The bones found in a place in Ethiopia suggest that people who lived there had to adapt their diet and habits to survive after a super volcanic eruption.
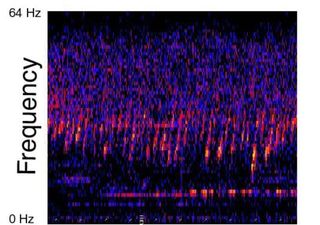
Since 1991, NOAA has been investigating the mysterious sounds of the ocean, including the enigmatic Upsweep, Bloop, Julia and Slow Down. Where do they come from?

This ambitious environmental DNA project promises to capture an unprecedented snapshot of global biodiversity and discover what is in the depths of more than 800 lakes.
Many cities have already reduced the pigeon population thanks to this innovative and ethical method. Birth control pills contain nicarbazin, which blocks egg formation in birds.

Study reveals that cumulus clouds dissipate quickly during eclipses. This effect could have implications for climate engineering that seeks to use aerosols to reflect sunlight and cool the Earth.

With more sunspots in sight, solar maximum is approaching and satellite and power grid operators will have to be prepared for various setbacks.

The United States expanded its underwater territory by almost 1 million km². The expansion protects their rights to marine resources and highlights the strategic incorporation of the Arctic.

From Argentina to Norway: the most famous travel magazine in the world shared the "Cool list 2024" where it announces the list of the 30 most interesting places and experiences to visit this new year.

This discovery is based on a new measurement of Earth's rotation made with a ring laser to measure microfluctuations in the planet's rotation speed.

Sustainable construction arrives with innovative concrete. A more sustainable cement binding material, developed by a company, promises to dramatically reduce CO2 emissions in the industry.

Dutch scientists found remains of a tectonic plate that had been searched for decades. Pontus occupied 25% of the Pacific Ocean and was a missing piece of Earth's geological puzzle.

Unlike other insects, bumblebees have proven to be skillful defenders against attacks by Asian hornets, using a unique technique to protect their colonies.
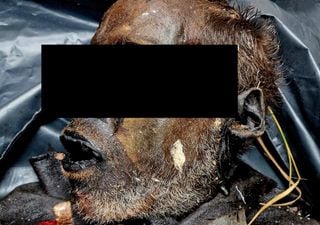
In a corner of Sofia, Bulgaria, an enigma that defies logic and science itself has been unravelled: a man who had disappeared for just 16 days was found in a state of complete mummification.

The emblematic tree was visited by thousands of tourists every year due to the popularity it acquired when appearing in a movie. It was located next to Hadrian's Wall.