
A new study reveals a rare tooth discovered in a North Dakota fluvial deposit, alongside a T.rex tooth and a crocodilian jawbone.

A new study reveals a rare tooth discovered in a North Dakota fluvial deposit, alongside a T.rex tooth and a crocodilian jawbone.

A subtle change in how climate risk is communicated can significantly increase attention to disaster preparedness messages, according to research by experts in Sweden and the US.

AI has garnered a reputation as an energy-guzzling monster of late, with data centres blamed for added emissions. But fresh research suggests otherwise, and it could actually help drive greener innovation

A cosmic trip could help bacteria protect future space missions from radiation but also find uses here on Earth too.

What if the secret to the brain’s remarkable ability to learn quickly lies in tiny, reusable mental building blocks? Scientists now believe these “cognitive Legos” help us master new skills with ease, offering fresh insight that could transform AI development and treatments for brain disorders.

A new study creates a novel, non-invasive way to monitor hormones in frog populations.

Scientists simulated the future of plastic floating in the water column to estimate how long it would take to remove these wastes from the ocean surface.

A new study describes one of the most species-rich marine vertebrate communities from the beginning of the age of dinosaurs on the Arctic island of Spitsbergen.

It was believed that cats began interacting with humans in the Levant along with the dawn of agriculture. New DNA evidence suggests that the timeline is off by a few thousand years.
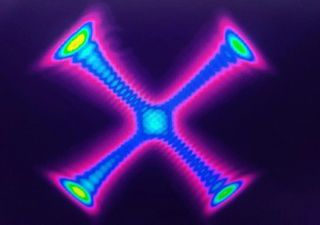
A new EU-funded project will train specialists to turn exotic “vortex” beams into real-world tech

Scientists monitoring the hole in the ozone layer are hopeful that it is recovering, following latest satellite data on its size and duration.

New research suggests exposure to PM2.5 can reduce the health benefits of exercise; we find out how.