A star that became famous in recent years for being at the end of its life has a confirmed companion in a new study.

A star that became famous in recent years for being at the end of its life has a confirmed companion in a new study.

Is there a turtle holding four elephants on which the Earth rests? Or perhaps it is a huge Titan carrying the entire planet on his shoulders? Here we explain it.

A new study warns that lunar landings could contaminate the Moon’s oldest ice. Methane from rockets disperses quickly and accumulates in regions that are key for science.

NASA’s Artemis programme has faced further delays, pushing back plans to return astronauts to the Moon, while China is accelerating its own lunar ambitions, including long term plans to establish a permanent base on the Moon, intensifying the global space race.

Operational for just a few months, the new Vera Rubin Telescope in Chile has officially begun its scientific operations with the exceptional discovery of an asteroid the size of eight football fields that rotates on its axis in just over 100 seconds.

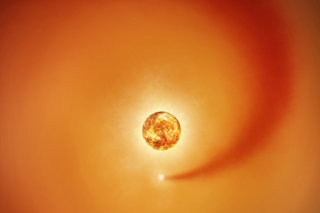
Astronomers from the University of Warwick and Durham University have detected an unusual shockwave surrounding a dead star, prompting new questions about what powerful event or process could have triggered this dramatic structure in deep space.

A group of astronomers has discovered that young galaxies already contain more heavy elements than previously thought, such as carbon and oxygen. In addition, their structure appears to be more advanced than was assumed in the early stages.

The mission was successfully launched this Sunday, January 11. NASA’s high-precision Pandora space telescope satellite will make it possible to study exoplanets and search for life beyond the solar system.

In new data obtained by the Hubble Space Telescope, an object that appears to be a relic of an ancient galaxy has been discovered.

For centuries we treated the Sun as a permanent fixture in the sky. Modern astrophysics disagrees, mapping out when it will die – and how Earth will fade long before.

After reaching an incredible speed of 109,000 km/h at perihelion—its closest approach to the Sun—on January 3, Earth is now slowing down over the next six months, before starting the race all over again.

At one time, scientists couldn’t see the far side of the sun, but a solar orbiter broadened perspectives and observed one of the strongest magnetic storms in 20 years.